IgA NEPHROPATHY
Symptoms and Treatments
Get Care
IgA Nephropathy Nephropathy refers to damage, disease , or other abnormalities of the kidney. IgA nephropathy is a kidney disorder in which antibodies to a protein called IgA build up in kidney tissue.
It is also called Berger’s disease.
IgA is a protein that helps the body fight infections. IgA nephropathy (Berger’s disease) occurs when too much of this protein is deposited in the kidneys. IgA builds up inside the small blood vessels of the kidney. Structures in the kidney called glomeruli become inflamed.
IgA nephropathy (Berger’s disease) is a form of mesangial proliferative nephritis.
The disorder can appear suddenly (acute), or progress slowly over many years (chronic glomerulonephritis).
Risk factors include:
- A personal or family history of IgA nephropathy or Henoch Schonlein purpura, a form of vasculitis that affects many parts of the body
- Caucasian or Asian ethnicity
Symptoms
There may be no symptoms for many years.
Symptoms include:
- Bloody urine that starts during or soon after a respiratory infection
- Repeated episodes of dark or bloody urine
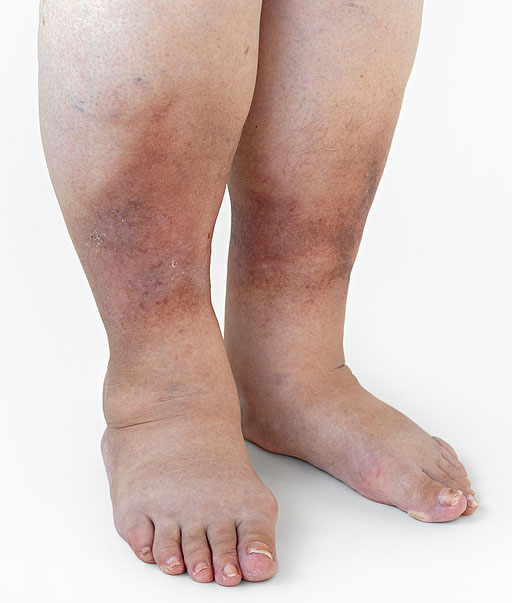
- Hand and feet swelling
- Symptoms of chronic kidney disease
Treatments
The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms and prevent or delay chronic renal failure.
Medicines may be given to control high blood pressure and swelling (edema). Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are used. Controlling blood pressure is the most important measure to delay kidney damage.
Corticosteroids, other immunosuppressive drugs, and fish oil have also been used to treat this disorder.
Salt and fluids may be restricted to control swelling. A low to moderate protein diet may be recommended in some cases.
Some people will need to take medication to lower their cholesterol.
Eventually, many patients must be treated for chronic kidney disease.
To learn more about IgA Nephropathy, please visit the Mayo Clinic Website at
IgA nephropathy (Berger’s disease) – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
